Prostatitis refers to prostate-specific and non-specific infection caused by acute and chronic inflammation, causing systemic or local symptoms. Prostatitis can be divided into non-specific bacterial prostatitis, idiopathic bacterial prostatitis (also known as prostate disease), specific prostatitis (from Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, fungi, parasites, etc.), non-specific granuloma Prostatitis, and other pathogens (such as viruses, mycoplasma, chlamydia, etc.) caused by prostatitis, prostate congestion and prostate pain.expander_maker more=”Read more”
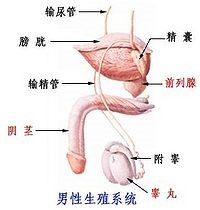

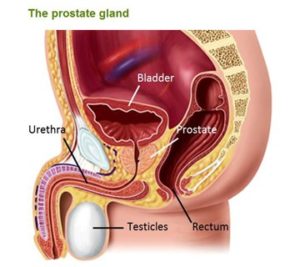
Etiology
One of the reasons: prostate congestion。
Sexual factors. Sexual life too frequent, forced interruption of sexual intercourse, can make the prostate is not normal congestion.
Direct compression perineum. Riding a bike, riding, sedentary, etc. can lead to repeated perineal damage and prostate congestion, especially in a long time riding the most common bike.
Unhealthy lifestyles.
Excessive or too frequent external stimuli, such as inappropriate prostate massage and other medical behavior.
Cold. Cold can cause the body’s sympathetic nervous excitement, resulting in increased pressure within the urethra, prostate tube contraction and impede the excretion of prostatic fluid, resulting in siltation or congestion.
The second incentive: urine stimulation
Medically known as chemical irritation from urine. According to reports, the urine contains a variety of acid-base chemical substances, when the patient local neuroendocrine disorders, causing posterior urethral pressure is too high, the prostate tube opening injury, it will cause irritation of uric acid and other chemical reflux into the prostate , Induced chronic prostatitis.
The third incentive: pathogenic microbial infection
A variety of micro-organisms such as bacteria, protozoa, fungi, viruses, etc. can be caused by the source of infection of prostatitis, which bacteria is the most common, such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, non-Neisseria gonorrhoeae. There are three major pathways of bacterial invasion. First, blood infection, clinical found that more than 90% of bacterial prostatitis is due to microbial infection. Second, lymphatic infections, such as lower urinary tract infection and colon, rectal inflammation can be infected through the lymphatic duct and prostate, resulting in inflammation. Third, the direct spread of male urination, the urine to go through the prostate, urine bacteria can be directly into the prostate, leading to prostate infection.
The fourth incentive: anxiety, depression, fear
Experts found that 50% of chronic non-bacterial prostatitis patients with anxiety, depression, fear, pessimism and other symptoms of excessive tension. Accompanied by pain and neurasthenic prostate patients often exaggerated physical discomfort and pain, often more than the actual symptoms of symptoms, this situation is known as “tension type prostatitis.” And psychological factors and the size of the age, young patients with mental burden was significantly heavier than the older patients, this situation often directly affect the effect of drug treatment.
The fifth incentive: immune factors, allergies
Studies have shown that chronic prostatitis and autoimmune factors have a certain relationship. Some experts have found in some arthritis patients, “anti-prostate antibodies,” the existence. These patients are often due to congenital or acquired immunodeficiency and anti-prostate antibodies, resulting in prostate tissue damage. If the patient after examination did not find evidence of bacterial, viral, mycoplasma infection, can consider the presence of immune factors.
Clinically, an allergic reaction to a virus can also lead to inflammation. In particular, some patients with low resistance to the body, the higher the sensitivity of the virus, easy to induce chronic prostatitis.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms varied, the severity is also different, some can be asymptomatic, and some are whole body discomfort. Common symptoms generally have the following aspects.
1, urinary discomfort: there bladder irritation, such as urinary frequency, urination, urinary tract burning, pain and radiation to the penis head. Early morning urethra may have mucus and other secretions, but also the feeling of dysuria.
2, the local symptoms: posterior urethra, perineal and anal bulge discomfort, squatting, stool and prolonged sitting on the chair stool pain increased.
3, radioactive pain: chronic prostatitis pain is not limited to the urethra and perineum, but also to its nearby radiation, the following low back pain is the most common. In addition, the penis, spermatic cord, testis scrotum, lower abdomen, groin area (thighs), thighs, rectum, etc. can be affected. It should be noted that chronic prostatitis caused by low back pain in the lower back, and orthopedic reasons such as back pain such as myofascitis, lumbar muscle strain, although easily confused, but the latter in the vicinity of the belt, prostatitis caused by low back pain High, can be identified.
4, sexual dysfunction: chronic prostatitis can cause loss of libido and ejaculation pain, ejaculation premature disease, and affect the quality of semen in the urination or stool can also occur when the urethral orifice white, combined with seminal vesicle can occur when the blood sperm.
5, other symptoms: chronic prostatitis can be combined with neurasthenia, showing fatigue, dizziness, insomnia; long-lasting prostate inflammation can even cause the body’s allergic reaction, conjunctivitis, arthritis and other diseases.
Complication
Acute prostatitis
1, acute urinary retention: acute prostatitis caused by local congestion, swelling, oppression of the urethra, resulting in difficulty urinating, or cause acute urinary retention.
2, acute vesiculitis or epididymitis and vas deferens inflammation: acute inflammation of the prostate is very easy to spread to the seminal vesicle, causing acute vesiculitis. At the same time bacteria can be reversed through the lymphatic vessels into the vas deferens wall layer and sheath to cause epididymitis.
3, spermatic lymph node enlargement or tenderness: prostate and spermatic lymphatic vessels in the pelvic traffic, acute inflammation of the prostate when the spermatic cord, causing spermatic cord lymph nodes and accompanied by tenderness.
4, sexual dysfunction: acute inflammation, prostate congestion, edema or a small abscess formation may have ejaculatory pain, painful erection, loss of libido, sexual intercourse pain, impotence, blood sperm and so on.
5, other: severe acute prostatitis may be associated with pain in the groin, severe cases may have renal colic.
Chronic Prostatitis
1, chronic vesiculitis: chronic prostatitis is the most common complications. In the course of chronic disease, the two often exist at the same time, affect each other. For a long time, can significantly lead to male sexual dysfunction.
Second, impotence: chronic prostatitis is a common complication.
Third, infertility: In infertility, chronic prostatitis is a very important reason.
4, posterior urethritis: chronic prostatitis and more complicated posterior urethritis, especially caused by urinary tract infection caused by prostatitis. In the clinical evidence, often with urinary tract irritation symptoms of chronic prostatitis, the first symptom.
5, epididymitis: prostatitis and seminal vesicle at the same time, inflammation can be invaded and epididymis caused by chronic epididymitis inflammation.
6, various types of bladder blister inflammation: When the prostate chronic inflammation spread to the bladder, there obvious symptoms of urinary tract irritation, is due to various types of cystitis.
7, bladder neck sclerosis: such complications are relatively rare
8, allergic diseases: chronic lesions lurking in the body for a long time, as allergens, causing all types of allergic diseases such as arthritis, myositis, iritis, neuritis.
The main factors of difficult to cure prostatitis
- Patients with foreskin is too long or phimosis;
- Before and during treatment there are still unclean sexual contact history;
- Sexual partners did not give simultaneous treatment;
- Combined with prostate stones;
- Abuse of antibiotics;
- A variety of pathogens mixed infection;
- Resistant strains increased;
- Secretion of prostatic secretion;
- Local anatomical characteristics of the prostate.